Share this article via Social Media: ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()

![]()
USB Standard
Universal Serial Bus (USB) was introduced in 1996 as a standard for connecting computer peripherals.
With this standard it is easier to connect and control external devices such as a mouse, keyboard, or digital camera with the computer. USB is designed with a 4-pin connection where both data and power transfer can take place.
Today we see computers usually equipped with one or two USB 3.0 ports, with or without the addition of USB 2.0 ports.
A wireless mouse and keyboard does not require much data / power and can easily operate via USB 2.0. With SuperSpeed USB 3.0, data can be transferred quickly. A great combination that is enough for many people .... or not?
With the developments of recent years where increasingly heavier external equipment (such as external data storage ) and more data (eg FullHD or 4K photos and films) must be transferred and mobile devices like to be loaded as smartphones , USB was also developed by in the form of USB 3.1
Due to the increase in computer peripherals and the corresponding demand for technical capacity, your laptop or PC may have too few USB ports available. Strengthened by the trend that manufacturers of, for example, laptops want to offer increasingly compact models, various connection possibilities disappear. A USB hub then offers a solution.
In the search for a suitable USB hub , you will soon encounter different terms, specifications, connections and prices. On this page we try to clarify and explain this for you, so that you can choose the perfect USB hub for your purposes.
To start right away, a USB connection consists of two parts which are not necessarily connected to each other. USB has a specific (technical) specification and a type of connector. The USB version specifies the technical limits of the USB port, such as amount of power and data speed. The type of connector tells which type of port it can be connected to. First let's look at the different USB versions. Later in these articles we return to the type of connector.
USB specification
In 2000 USB 2.0 came and 8 years later USB 3.0 was introduced.
USB 3.0 is at least 20 times faster than USB 2.0 (480Mbps) with a data transfer speed of 5 Gbps.
USB 3.1 is the latest development in the USB field. With a maximum data transfer speed of 10Gbps, it is twice as fast as USB 3.0.
Besides the difference in data transfer speed, there is also a difference in the current output. USB 3.1 delivers 2A (5v) and offers technical possibilities up to 5A / 20V, depending on the Power Delivery Profile. More power means in short that heavier peripherals can be connected. This also affects the charging of smartphones via USB .
In the table below you will find an overview of the USB versions and specifications. 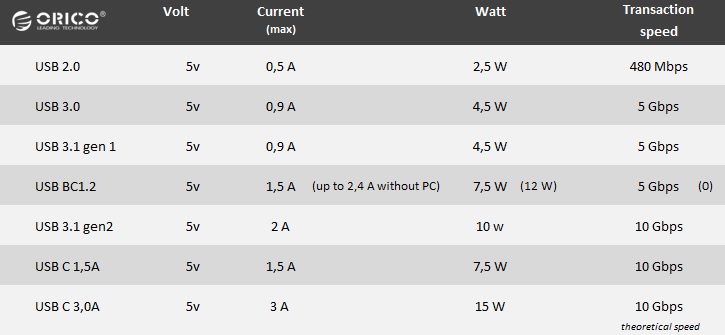
Different USB connections
In addition to the different USB versions, different connections are possible.
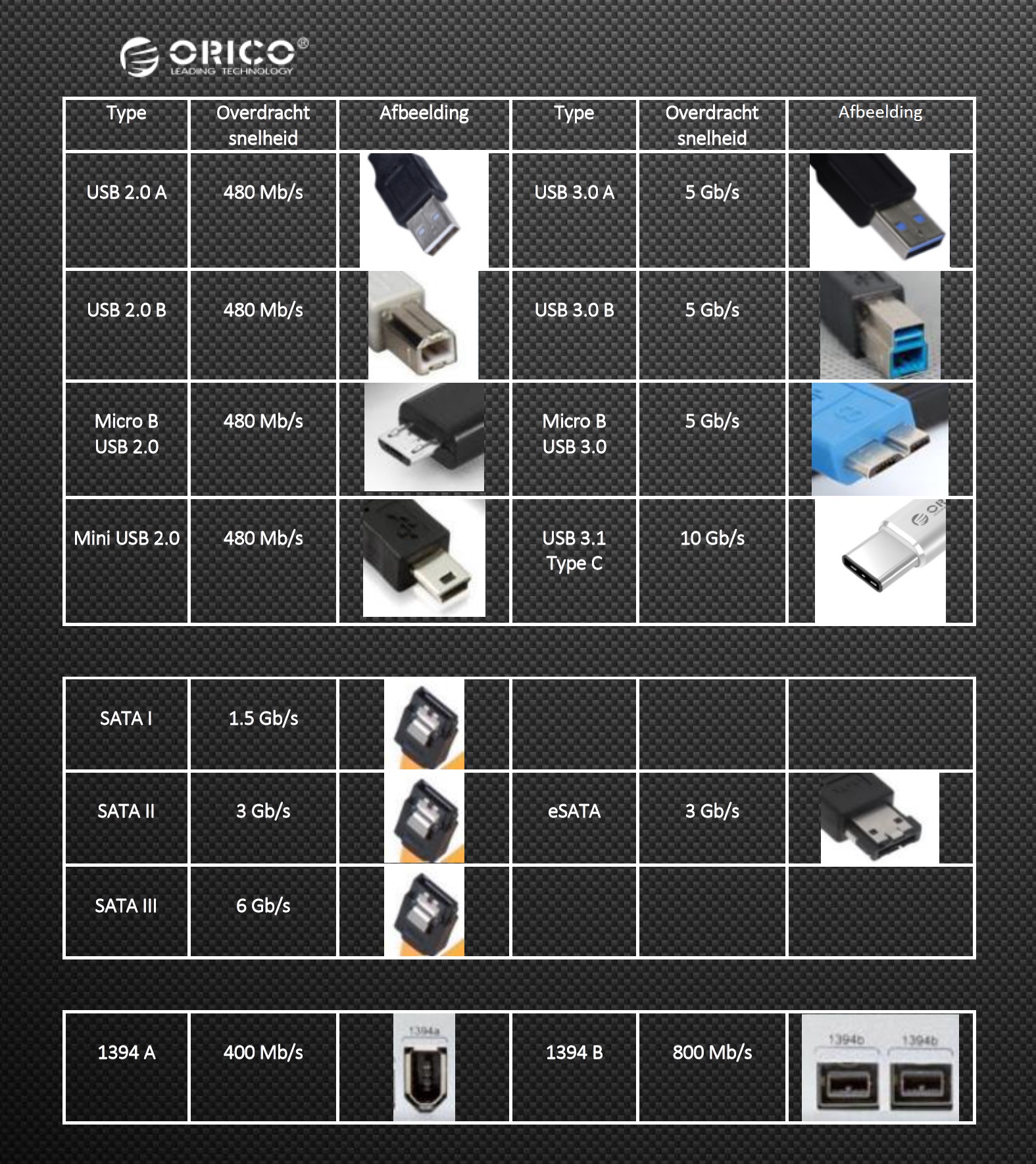
The Type A connection is the best known and is most common. In addition to Type A there is a Type B, which is designed for a more stable connection and we often see back at eg printers. For mobile applications, smaller type connections have been developed, such as the Mini and the Micro USB. With the advent of USB 3.1 we also see a new connection, the Type C.
As shown in the image below, different USB versions with different USB connectors are possible. For example, the most commonly used USB type A connector can be used with both USB 1.0, 2.0 and 3.0. With the USB type B and Micro B there is a clear difference between the USB 2.0 and USB 3.0 specifications.
The USB type C connector is often associated with USB 3.1 (gen 2), but Type C connecter is not unambiguously connected to USB 3.1 (gen2). For example, all contemporary (2017) smartphones with USB Type C are still according to USB 2.0 specification. There are also many Type C connections on new computers and laptops with USB 3.0 specifications.
The other way around, however, USB 3.1 (gen2) is only possible with Type C connector.
Share this article via Social Media:
Share this article via Social Media: